Embedded business intelligence (embedded BI) is the integration of self-service BI tools into regularly used business applications. Embedded BI provides an improved user experience with interactive data visualizations and real-time analytics and reporting. Instead of using a standalone application, embedded BI enables business intelligence directly within the applications an organization is already utilizing.
Benefits of Embedded BI
- Improves the user experience
- Higher user adoption than standalone analytics tools
- Improved business performance
- More effective data insights
- Leads to better decision making
Embedded BI also improves insights and metric reporting as it can work with multiple datasources. With the KPIs and other actionable insights available directly in the business applications, managers can make quicker and better strategic decisions.
All of which leads to better decision making, contributing to revenue growth.
From manufacturing to IT, retail, sales, finance, and healthcare, we'll discuss several use cases and how each industry uses embedded BI and analytics to improve business performance.
Using Embedded BI in Finance
Financial analysts need to review and track large amounts of numerical data such as investments, revenue, income, working capital, and assets. Embedded BI makes this process much easier by placing essential information from different sources into a single location.
For example, an analyst might need to analyze reports on accounts receivable and accounts payable, while tracking assets, liabilities, and investments at the same time. A financial report linked directly to the business unit's record allows an analyst to view all of this data in real-time.
Healthcare Embedded BI Use Cases
Incomplete information in patient charts can affect a variety of downstream processes such as treatment, billing, and insurance. Jumping through different medical record systems to get to lab results and treatment plans means wasted time and possibilities of errors. Embedding the report generation within applications like patient EMRs allows BI to reduce the time need to access complete patient information while still using a healthcare provider's existing business processes.
Embedded BI can also provide information and analysis from external sources directly inside the healthcare management system to help improve treatment plans, billing, insurance, and more.
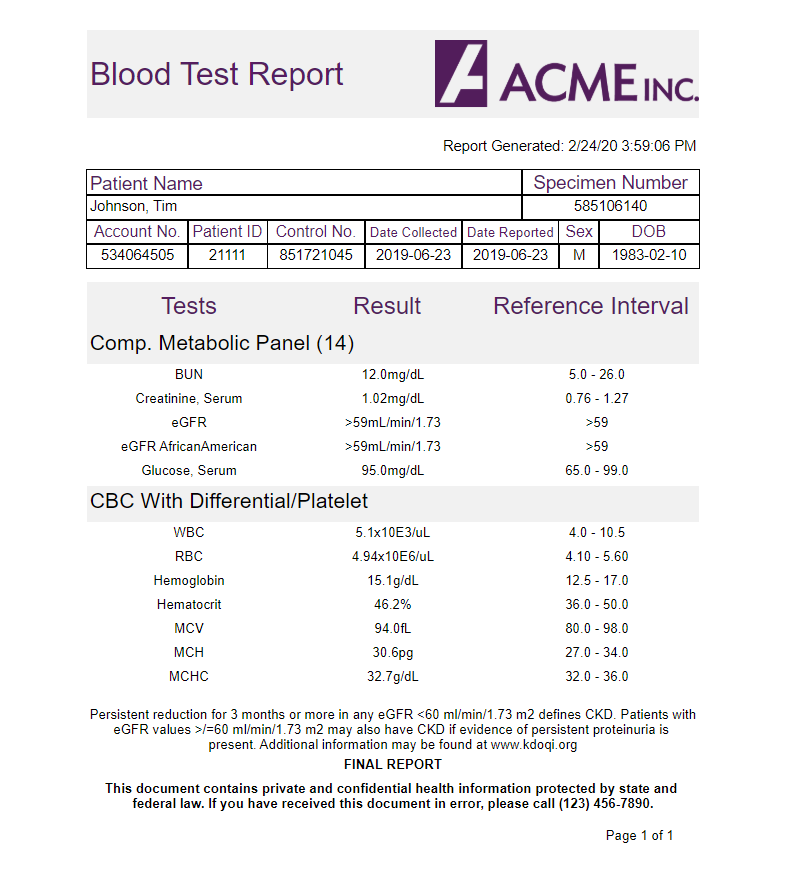
Embedded BI in the Insurance Industry
Many tactics are used to commit insurance fraud, including staging incidents and falsifying information. Embedding BI in a claims management program allows insurance companies to use analytical models to determine possibilities of fraud without the need to review each claim manually. This capability can consider a variety of information to identify suspicious claims, including the claim amount, claimant history, location, and time of day.
The embedded BI can provide these fraud indicators to a claims processor or investigator as they are working through the claim. It can also cross-reference these alerts with publicly available information to reduce the number of false leads requiring investigation.
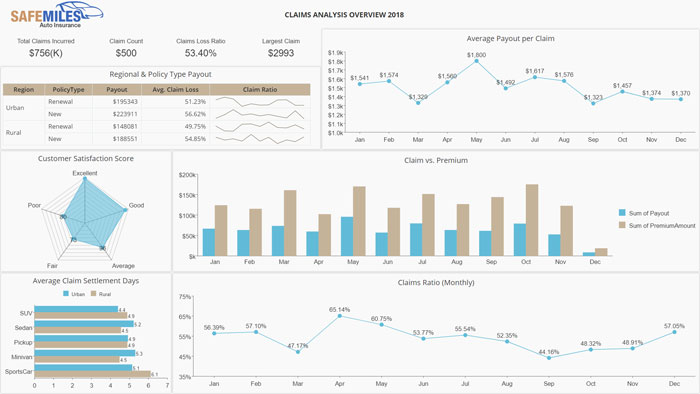
Embedded BI in Retail
The retail industry collects a tremendous amount of data in real-time from sources such as point-of-sale (POS) transactions, shopping carts, stock orders, and inventory levels. Embedded BI can help aggregate and analyze the gathered data to evaluate metrics like sales performance, staff efficiency, and stocking efficiency.
Embedded BI can help retailers suggest cross-selling and up-sells based on that customer's purchase history.
Additional uses of embedded BI in retail include a market analysis at the customer's level, allowing retailers to plan campaigns that target their audiences more precisely.
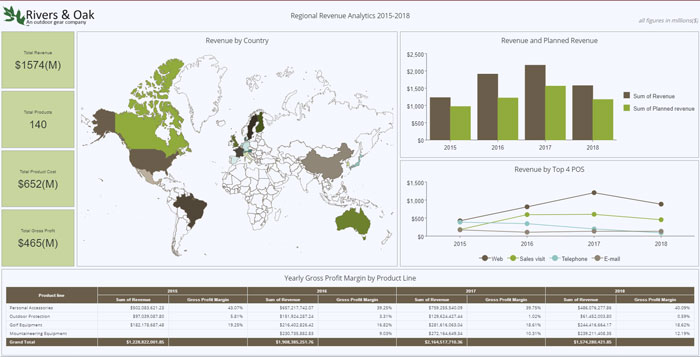
Embedded BI in Technology
Companies that provide Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) have historically experienced difficulty understanding their customer turnover, or churn, which is particularly high for this business. Standard churn applications typically provide only necessary information such as the number of customers that stopped using the service last month and the amount of revenue that was lost.
Embedding dashboards and reports inside a customer support portal allow product managers to make decisions considering many more factors such as customer demographics, service usage, and support history. Managers can then use this information to predict churn with greater precision and identify measures for mitigating it.
Adding Embedded BI Into Software
Today's organizations are increasingly likely to capitalize on the trend towards integrating BI into their existing software. The journey towards this goal often begins by making the decision to build BI in-house or buying a third-party solution. It may be surprising to learn that an organization with software development as a core competency is more likely to obtain embedded BI from a third-party than an organization that doesn't develop software.
Independent software vendors (ISVs) specialize in developing software like CRM, ERP, and financial applications. However, these organizations recognize that BI analytics is typically outside their expertise. ISVs are, therefore, more likely than general enterprises to buy embedded analytics functionality from a third-party.
Typical enterprises that don't develop commercial software products are more likely to build this functionality themselves. They have proprietary business applications that IT teams have already developed, including those intended for consumption by outside parties such as customers and suppliers. These organizations are often eager to immediately begin an in-house build of analytics functionality upon deciding they need embedded BI.
However, general enterprises should first consider the embedded analytics that is commercially available, like ISVs do. Third-party vendors are more likely to be experts in the latest BI technologies and trends, including predictive analytics, machine learning, and interactive visualization. Furthermore, buying embedded BI allows organizations to focus on their core competencies, allowing them to leverage the toolset to bring the BI capabilities to the users more quickly.

What to Look For in an Embedded BI Solution
Once you've decided to buy an embedded BI solution, you should carefully investigate its features. Organizations may have unique requirements, but they often need many of the same BI capabilities.
For example, white-label self-service BI allows users to customize a third-party product to fit the look and feel of the solution it embeds into. Embedded BI should also include an application programming interface (API), which allows the business application to use custom hooks when embedding the BI capabilities. Furthermore, a third-party solution should enable users to design an interface (UI) and user experience (UX), eliminating the need to embed the entire BI product.
Scalability is also a vital characteristic in a BI solution, especially for an enterprise. In particular, the scale of the solution's operations must be able to increase quickly in response to an increase in its user base.
A third-party BI solution should also use a clear and straightforward licensing model, allowing organizations to quickly calculate the solution's total cost of ownership (TCO). It's also vital that the TCO not become cost-prohibitive as its operation scales up.
Users must also be able to use the embedded BI aspect within their business software without needing to log in a second time. Businesses should ensure that the third-party solution they select has security extensibility, meaning the solution can inherit the authorization and permissions needed to access it from the business application. For example, SaaS-based applications with multiple tenants should be able to secure resources at the data level.
Understand the Story Behind Your Data
Need help making sense of your data? Wyn is a web-based BI and data analytics platform that provides greater insight into your data.
Wyn offers built-in tools for report and dashboard creation, data governance, security integration, embedded BI, automated document distribution, and a business-user friendly interface for self-service business intelligence.




























