Over the past several years, the 3D Model has revolutionized the business world. Developed to cater to the specific needs of industries such as TV, Advertisements, Architecture, and Manufacturing, it has become a common name and an essential tool for every industry irrespective of size and nature of business operation such as education, sports, science, space, healthcare, medicine, automobiles, manufacturing, construction, entertainment, gaming, animations, and many more.
Wyn Enterprise offers to work with 3D Models in the BI Dashboard, providing a whole new experience of visualizing important insights within your data and making much more impactful business decisions.
In this blog, we’ll learn about these 3D Models and how you can display them in WynDashboards, under the following topics:
- What is a 3D model?
- Why do industries use 3D models?
- 3D model in BI Dashboard
- Working with 3D models in Wyn Enterprise
- 3D models
- 3D Scene Designer
- 3D Scene Visual in WynDashboards
- Conclusion
What is a 3D model?
A 3D Model is a three-dimensional digital representation of an object or a surface generally made using specialized UI-based software such as CAD, AutoDesk, or 3D Max or API-based frameworks such as Babylon.js or Three.js.
The 3D Model is formed by connecting polygons along edges in a virtual space. The polygon represents an enclosed area (or face) by joining the points (or vertices) in the 3D coordinate plane. The collection of these polygons is known as a Mesh, and it forms the fundament building block of 3D modeling as shown in the image below:
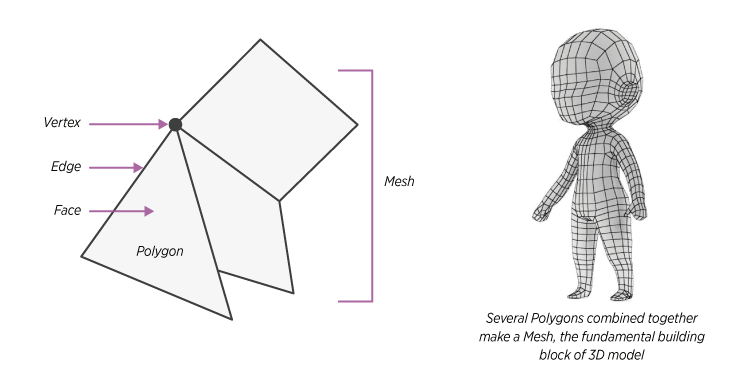
To make the mesh look more realistic, the 3D modeling application allows several configurations such as,
-
Scene: holds and contains the elements of 3D Model(s) together.
-
Renderer: configure the fundamental settings of a scene such as the background color, size, and pixel aspect ratio.
-
Camera: provides the field of view, expressed in degrees from the bottom to the top of the visible area.
-
Lighting: highlights the details, shapes, and materials of your models.
-
Animation: provides an illusion of movement in the model.
Why do industries use 3D models?
The 3D Model lets industries visualize the idea and bring its design prototype to life but, on computer screens. It helps to generate a digital twin of an object and convey information about its size, shape, and texture. Thus, it finds its use in an array of business areas such as building concepts, ideas, goods, objects, processes, systems, or properties.
Many industries utilize 3D modeling for various projects due to the endless opportunities it offers. Some of the notable benefits it provides are:
-
speeding up the product design development process by bypassing to-and-fro movements with prototype designing for changes
-
early fix in product designs even before designing a physical prototype
-
improved visualization that lets the user preview the changes from every perspective, making it easier to confirm physical and functional alterations and refine aesthetic
-
smooth and seamless collaboration among engineers, designers, and every other team member, whether non-technical or technical, who needs to give input on the project’s design
-
saves money and automates the visualization process.
3D model in BI Dashboards
A 3D Model in a BI dashboard can help analysts add a different perspective to their visualization and present data against a 3D Model of their product, architecture, and so on. It eventually brings more clarity to data visualization and helps in robust decision-making.
It can be used to depict sales against locations in a Sales dashboard, display product configuration in a Product Launch Dashboard, units produced by each production line in a Production Management dashboard, and many more.
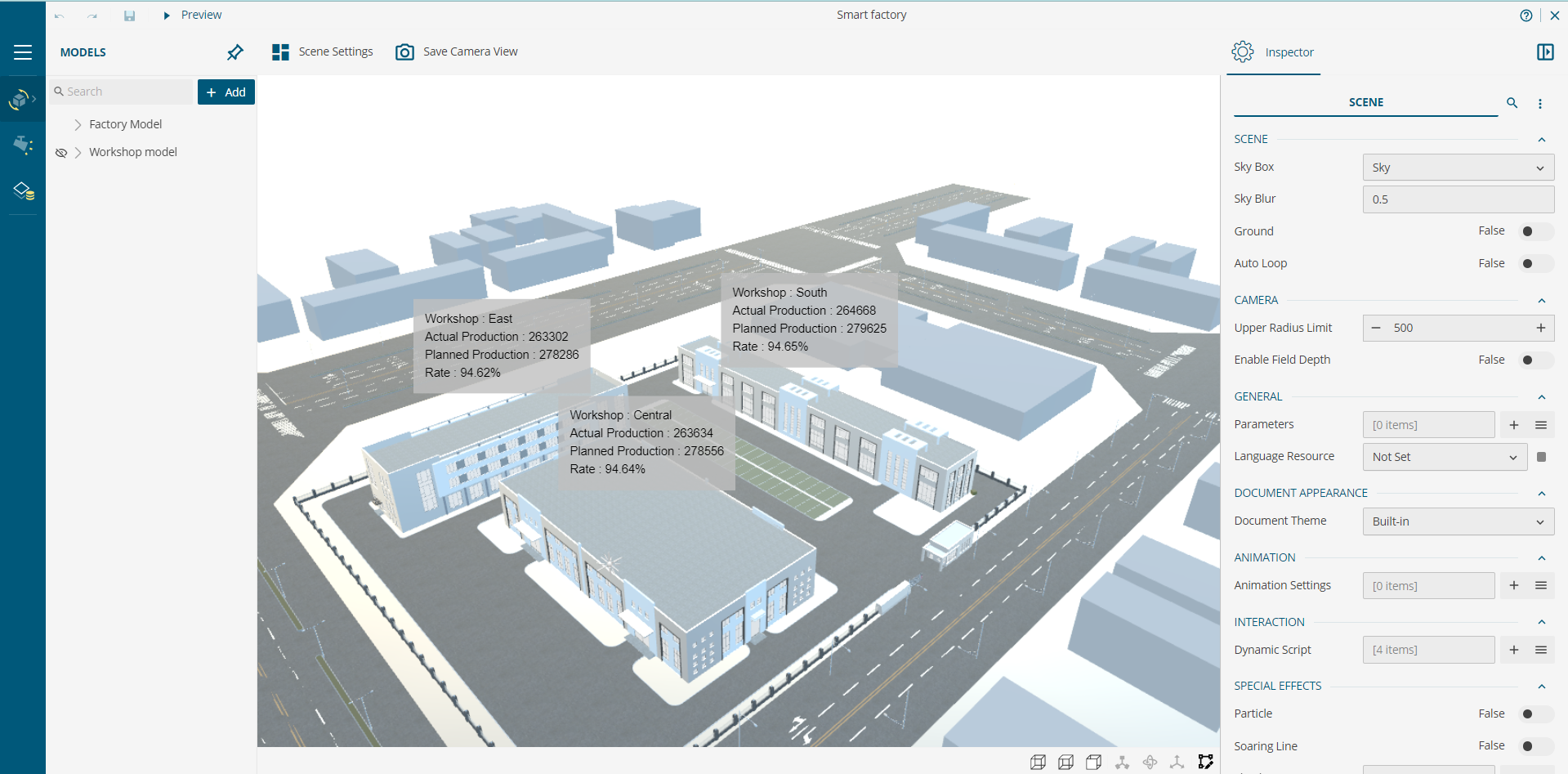
For example, in the Factory Management Dashboard below, we present the production data from different workshops in a factory on a 3D Model. It depicts clearly the information against the architectural location of the different workshops in a factory.
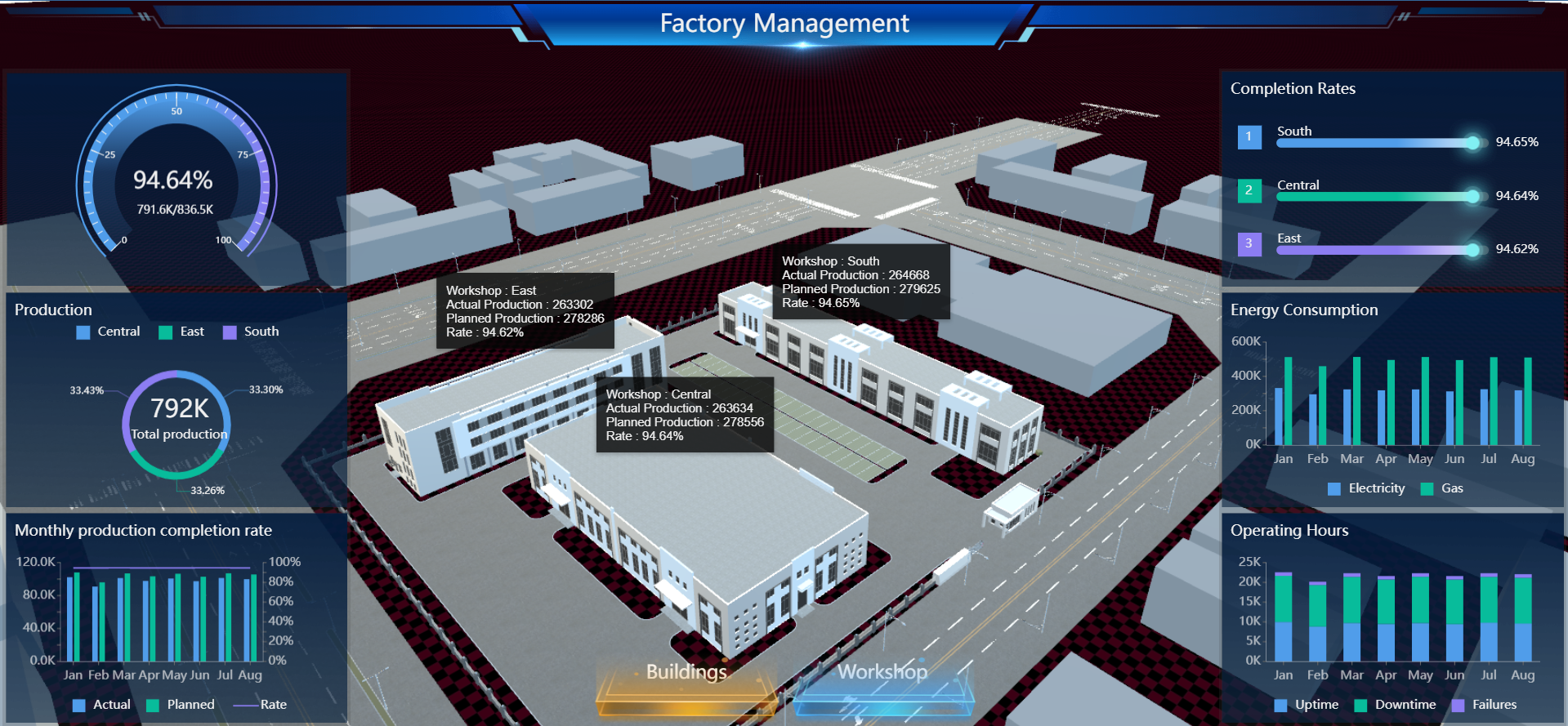
To see the 3D Factory Management Dashboard in action, please click here.
Working with 3D Models in Wyn Enterprise
With Wyn Enterprise, displaying business data against a 3D Model requires the creation of a 3D Scene visual that provides an environment to bind the 3D Model with the data source. The complete process for working with a 3D Model in Wyn Enterprise is depicted in the flow diagram below:
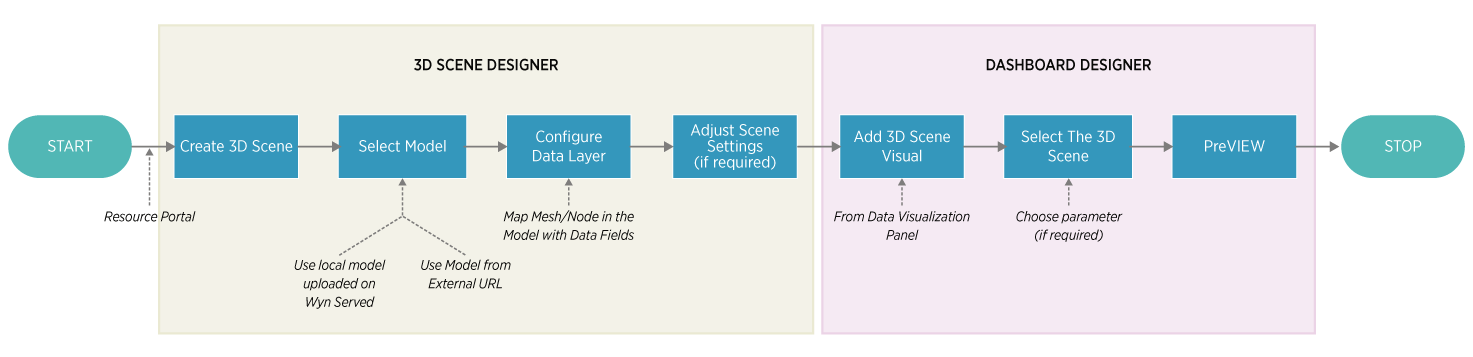
It majorly includes a .glb-based 3D Model, a 3D Scene Designer, and a 3D Scene visual in the WynDashboards designer.
3D models
3D Models can be used in two ways within the Wyn Server, one uploading a local copy to the Wyn Server from the Resource portal and another using the External URL directly in the 3D Scene Designer.
The uploaded Model appears under the 3D Model node of the Resource Portal as shown below:
You can categorize, rename, delete, or download the model from the resource portal.
Currently, the Wyn Server supports GLB (.glb) format for 3D Models. This is because the glTF format is recommended format when you want to transmit 3D Scene data efficiently over the internet for viewing in a remote application.
Note: (we’ll support other popular formats such as 3ds, FBX, and others in the future)
For more information on 3D Models, refer to the documentation.
3D Scene Designer
3D Scene Designer allows the creation of the visual for the WynDashboards. It offers the environment to configure one or more 3D Models to make them realistic with settings such as adding lighting, configuring scene settings, adding animation using the dynamic script based on Babylon.js, mapping model mesh objects with dataset fields, and much more. It looks as shown below:
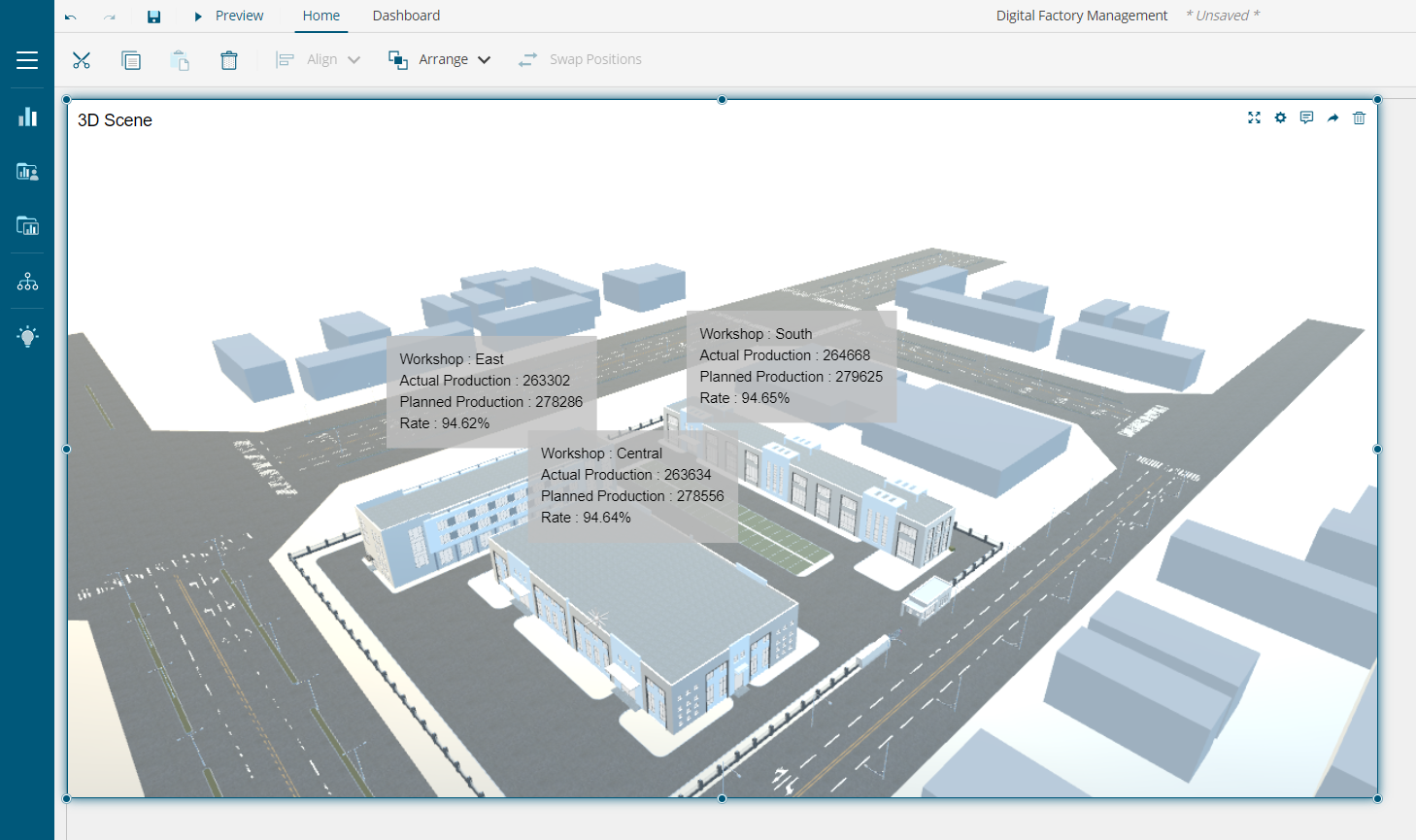
Data from a dataset is mapped to the 3D Model’s mesh/node from the Data Layer as shown below:
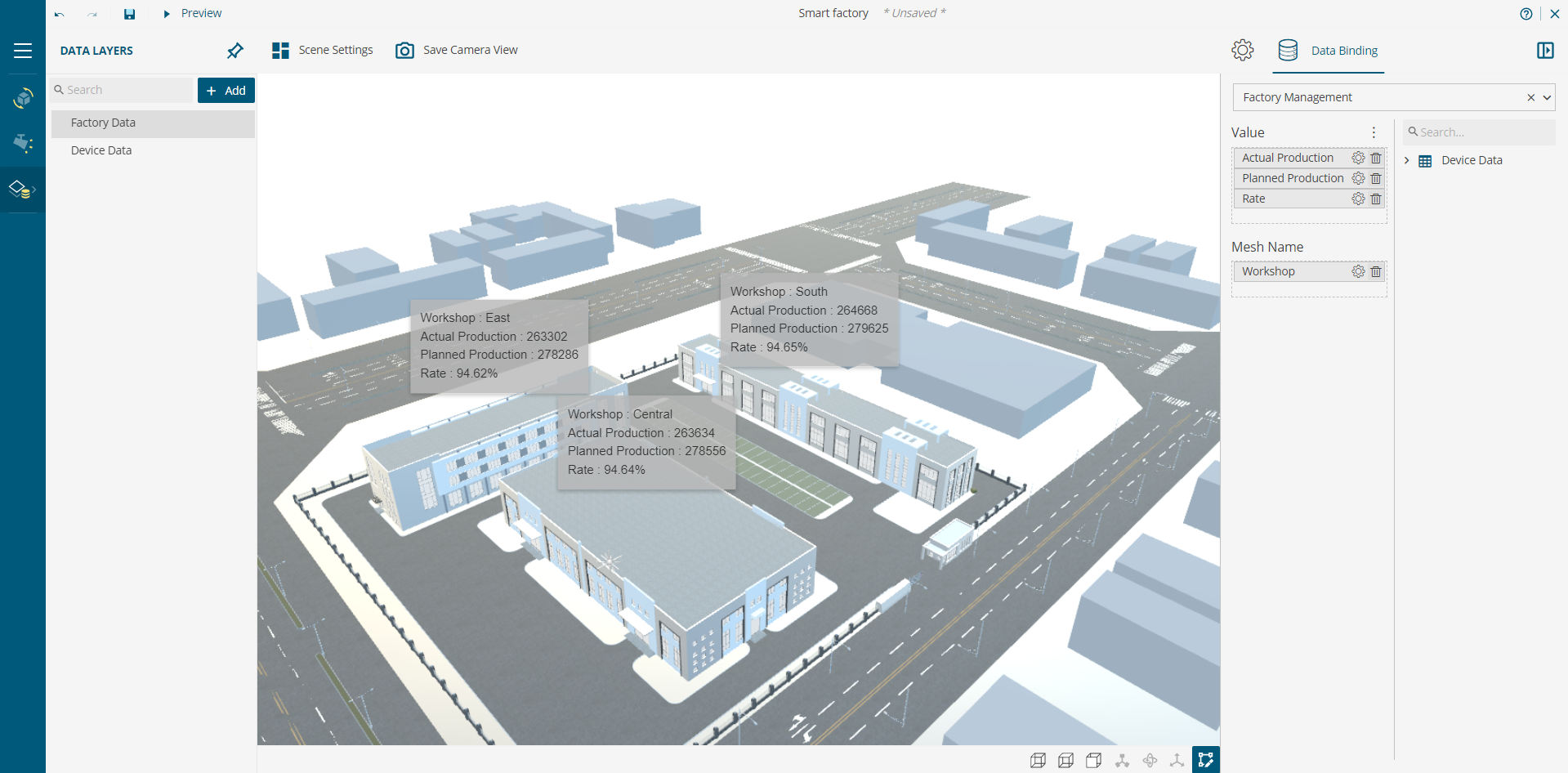
To learn about the components of 3D Scene Designer in detail, check out the user guide.
3D Scene Visual in WynDashboards
Once you have the desired 3D Scene with you, add it to the WynDashboards using the 3D Scene visual, which you can find within the Charts section in the Data Visualization panel.
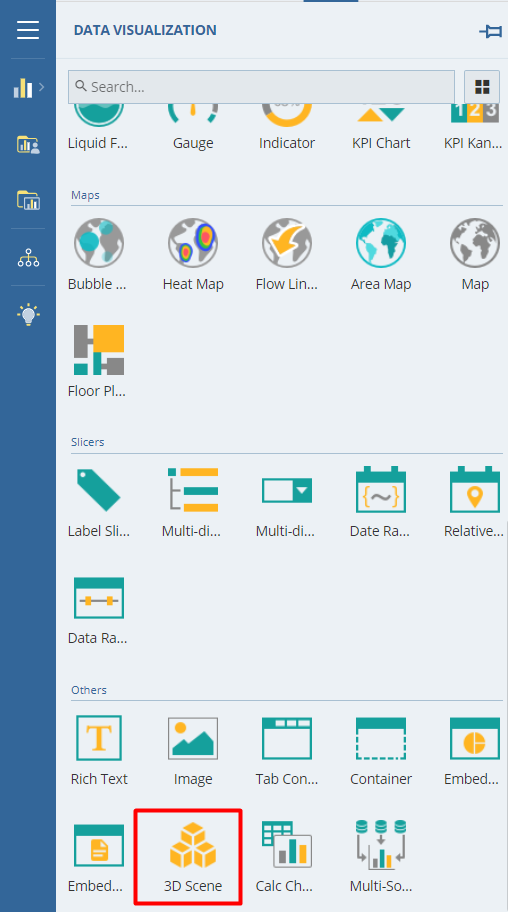
When you drag and drop the visual from the panel to the design surface, you will be asked to configure the 3D Scene for this visual. In the 3D setting dialog that opens, choose the desired scene and provide the parameters (if required).
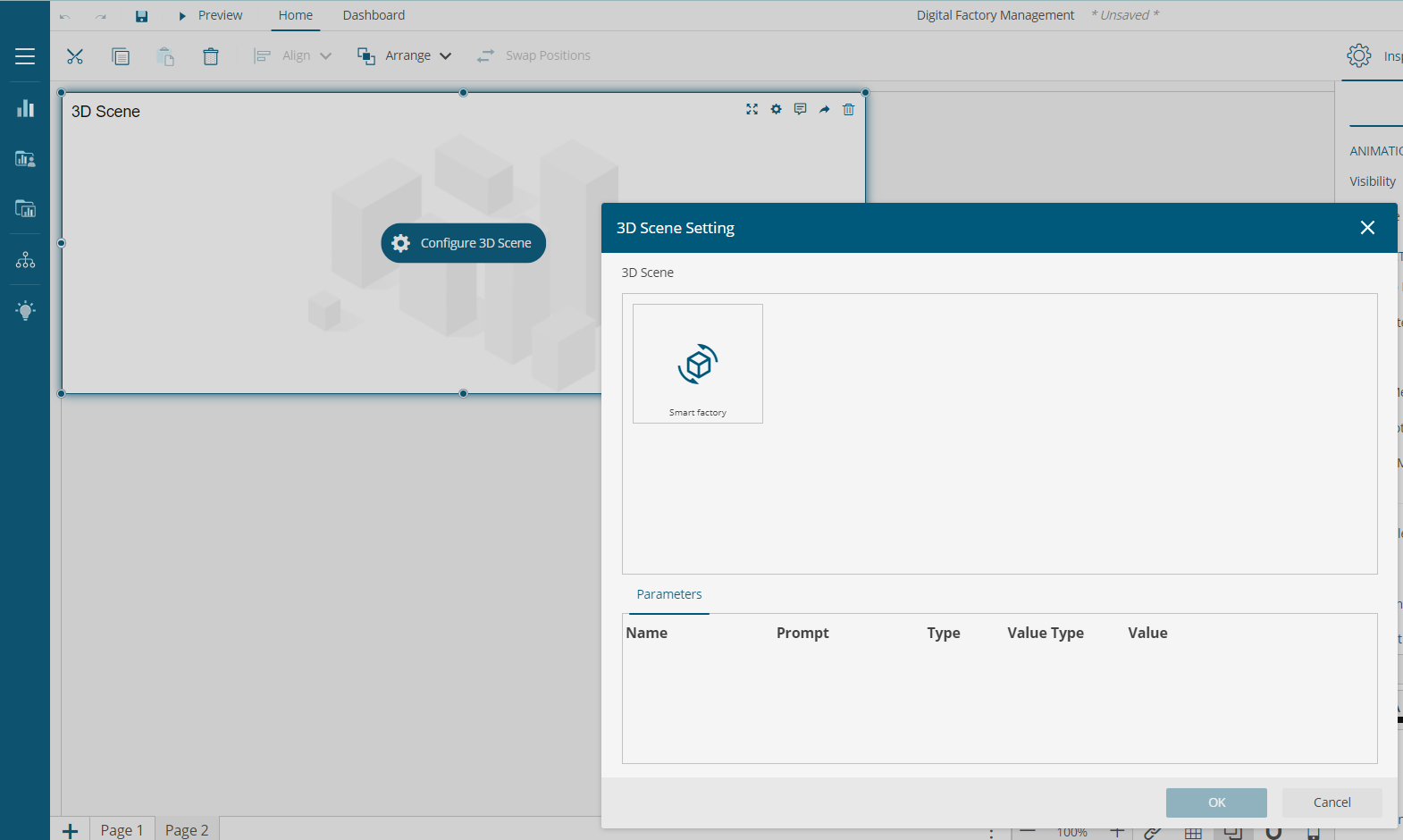
The 3D Scene is loaded in the dashboard visual and appears as shown below: